Strategy
Hearing care market
and supply chain
Hearing – an underestimated topic
The importance of good hearing and the consequences of hearing loss continue to be underestimated, even though according to the World Health Organization (WHO), about 15% of the world’s population is affected by hearing loss. The number of people with hearing loss continues to rise, due both to the aging of populations in developed countries and to growing noise pollution in our environment. In addition, according to the UN children’s fund UNICEF, over 665,000 children are born with significant hearing loss each year.
People with untreated hearing loss are often faced with serious consequences. These range from disadvantages at work to relationship problems and social isolation, which may even lead to depression. Especially severe are the consequences for children with untreated hearing loss, as the development of speech and language is fundamentally dependent on the sense of hearing. Untreated hearing loss also is often associated with academic underachievement, which can lead to lower job performance and fewer employment opportunities later in life.
In addition to the impact of hearing loss at an individual level, untreated hearing loss puts a heavy cost burden on society. Unaddressed hearing loss costs countries an estimated USD 750 billion annually in direct health costs and loss of productivity. Today’s hearing technologies offer the opportunity to reduce this significantly.
Market opportunities
The hearing aid market continues to grow, driven by long-term socioeconomic forces. The number of people on our planet will continue to increase. Although populations in developing countries are expected to grow the most, even developed countries with stable populations will face a growing proportion of elderly citizens, who are likely to experience hearing loss. These trends create commercial opportunities for Sonova through an increase in demand for hearing care.
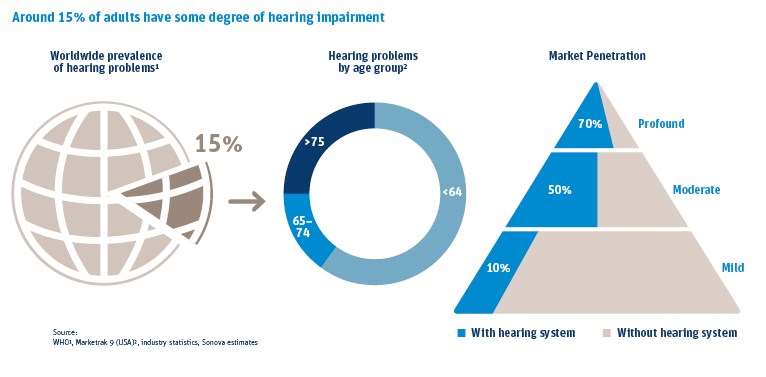
The overall rate of penetration for hearing technologies in developed countries is around 20%. We estimate that, while in developed markets 70% of people with severe-to-profound hearing loss have hearing aids, only 10% of those with mild-to-moderate hearing loss currently use hearing instruments. However, younger and less-affected people are increasing their adoption of hearing aids as technology moves toward ever better sound quality and smaller, more discreet devices.
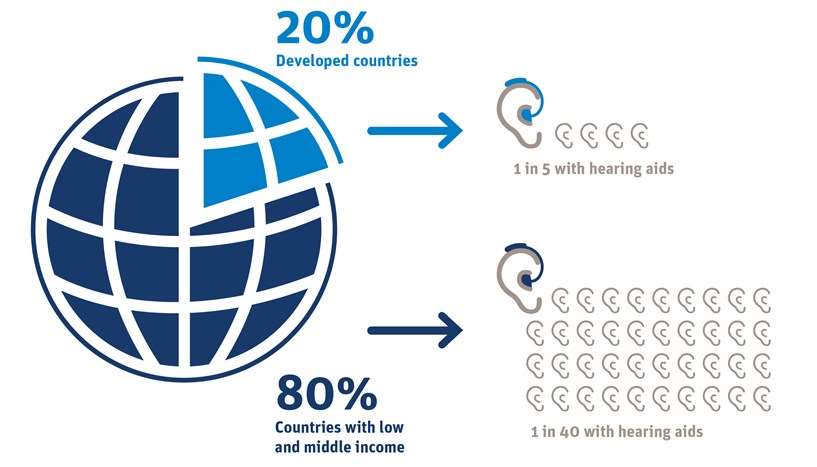
Around 80% of people with hearing loss live in developing countries with low to medium income. The hearing care market in developing countries remains relatively under-served: Only one in forty people with hearing loss wears a hearing aid. People in developing countries often have no access to audiological and medical care.
However, we expect the growth of the middle classes in emerging economies to boost consumption significantly and see the shift in spending power and lifestyle ambition as a substantial opportunity. Our strategy therefore calls for a strong focus on the potential of emerging markets to serve the demands of these newly-empowered consumers with suitable product formats.
The hearing care market is highly diverse, requiring a broad range of technologically-advanced solutions and extensive customer service channels. The core of Sonova’s innovation strategy is to maintain full development pipelines for products and solutions. By extending our innovative base technologies across the different businesses and maintaining our rigorous technology platform approach to product and solution development, we accelerate time-to-market, consistently generating around two-thirds of our hearing instrument sales from products launched within the previous two years.
Market challenges
Even though we offer a product portfolio with a wide range of performance and pricing levels, affordable hearing care is still a challenge for people in emerging countries and for underprivileged social groups in developed regions.
Changes to governmental reimbursement and subsidy regimes affect the amount of funding available to end-users and thus the number of hearing aids sold. This has a significant impact: regions with high reimbursement levels clearly show higher market penetration; the lower end of the market penetration table mostly comprises emerging countries with no reimbursement regimes.
This challenge is aggravated by the fact that many countries lack trained health personnel, educational facilities, and necessary data to address the needs of those living with hearing problems. These factors, and the lack of hearing care professionals and infrastructure in certain markets, can impede efforts to raise the penetration rate. As an example, China faces the challenge of the rapidly-growing number of people with hearing loss potentially exceeding the number of qualified hearing care professionals to help them. To tackle these challenges, we have defined a wide range of initiatives, including dedicated products for China, co-operation with distribution partners and government, and education for hearing care professionals. Read more about our commitment in the section “Access to hearing care”.
International supply chain
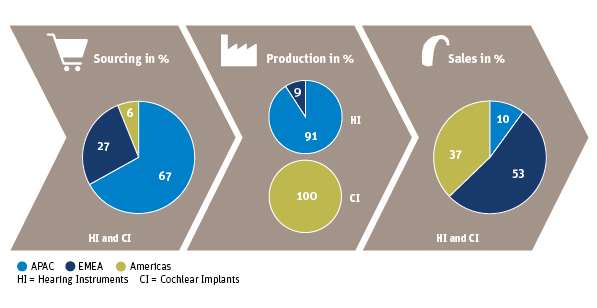
Sonova deals with around 430 suppliers to its hearing instruments segment, who deliver components for manufacturing and assembly, and around 120 direct material suppliers to the cochlear implant segment. In spending terms, 67.1% of Sonova’s purchase volume is located in the Asia/ Pacific region, 10.2% in Switzerland, 15.6% in Europe (excl. Switzerland), 6.3% in North America, and 0.8% in Africa.
Our suppliers are mainly high-tech design and component makers, or original equipment manufacturers with a high degree of automation. Sonova engages only a very small number of contractors and licensees. Sonova’s own manufacturing operations extend from fully-automated processes, such as hybrid circuit production, to highly-skilled manual work, such as assembly of hearing aids and cochlear implants.